HEALTH
Vaccination
The Samoyed is a very strong dog which lived in a hard and inhospitable habitat. It does not have a predisposition to disease, but even so we need to vaccinate it every year, deworming it every 04 months and making an external parasites control beyond frequent brushing.
After 21 days from the last dose of vaccine or the annual booster the animals are properly protected and because of that during that period: do not give it a bath or take it to walk to places where unknown dogs move. It is important to know that you should never put a dog that does not have all the vaccines on the floor of a veterinary clinic and always remember to use imported vaccines.
Basic Disease
Currently there are vaccines to help prevent many fatal diseases in dogs - and antibiotics to treat some diseases. With a suitable protocol of preventive vaccines, your Samoyed will probably never suffer from any of the diseases mentioned below, but we described them only as a precaution..
Always use imported vaccines and follow the protocol of vaccines oriented by a licensed veterinarian.
Kennel Cough - This is a respiratory infection where many dogs are kept together. The infection causes the trachea, the larynx and the bronchial tubes inflammation. The Bordetella bronchiseptica bacteria when infects a dog will develop a mild cough to severe sometimes with a runny nose five to ten days after exposure. It should be treated with antibiotics and rest. Prevention is the most sensible choice. If your dog has contact with many other dogs make sure it is protected against Bordetella. A liquid vaccine administered through the dog's nose combined with an injection for the canine parainfluenza virus.

Bordetella Bronchiseptica
Corona Vírus - It is a mild disease that is spread when a dog comes into contact with the feces or other excreta from other infected dogs. Such disease hardly will kill the dog and it is even hard on puppies or dogs that are not in the best of their health. The evidence of coronavirus are depression, lack of appetite or vomiting - especially if there is blood - and a bad period of diarrhea. If the stools have very strong smell, particularly with blood or a strange yellow-orange color, those are also signs. If the coronavirus is diagnosed, the veterinarian will recommend plenty of fluids to replace what was lost through vomiting and diarrhea as well as medication to help keep the vomiting and diarrhea at least. A vaccine against the coronavirus is usually recommended if your dog is finding many other dogs.
Corona Vírus
The Samoyed is a very strong dog which lived in a hard and inhospitable habitat. It does not have a predisposition to disease, but even so we need to vaccinate it every year, deworming it every 04 months and making an external parasites control beyond frequent brushing.
After 21 days from the last dose of vaccine or the annual booster the animals are properly protected and because of that during that period: do not give it a bath or take it to walk to places where unknown dogs move. It is important to know that you should never put a dog that does not have all the vaccines on the floor of a veterinary clinic and always remember to use imported vaccines.
Basic Disease
Currently there are vaccines to help prevent many fatal diseases in dogs - and antibiotics to treat some diseases. With a suitable protocol of preventive vaccines, your Samoyed will probably never suffer from any of the diseases mentioned below, but we described them only as a precaution..
Always use imported vaccines and follow the protocol of vaccines oriented by a licensed veterinarian.
Kennel Cough - This is a respiratory infection where many dogs are kept together. The infection causes the trachea, the larynx and the bronchial tubes inflammation. The Bordetella bronchiseptica bacteria when infects a dog will develop a mild cough to severe sometimes with a runny nose five to ten days after exposure. It should be treated with antibiotics and rest. Prevention is the most sensible choice. If your dog has contact with many other dogs make sure it is protected against Bordetella. A liquid vaccine administered through the dog's nose combined with an injection for the canine parainfluenza virus.

Corona Vírus - It is a mild disease that is spread when a dog comes into contact with the feces or other excreta from other infected dogs. Such disease hardly will kill the dog and it is even hard on puppies or dogs that are not in the best of their health. The evidence of coronavirus are depression, lack of appetite or vomiting - especially if there is blood - and a bad period of diarrhea. If the stools have very strong smell, particularly with blood or a strange yellow-orange color, those are also signs. If the coronavirus is diagnosed, the veterinarian will recommend plenty of fluids to replace what was lost through vomiting and diarrhea as well as medication to help keep the vomiting and diarrhea at least. A vaccine against the coronavirus is usually recommended if your dog is finding many other dogs.

Distemper - The death rate from distemper in dogs is greater than any other infectious disease. This is a highly contagious virus that spreads through direct contact or by air. A healthy dog can even survive distemper, but usually with sequels. However, if the immune system of your dog has no resistance, its whole body can be overwhelmed by viruses and as well as an opportunistic bacteria that take advantage to cause secondary infections.
Distemper usually happens in two phases. Three to fifteen days after exposure to virus, the dog develops a fever, poor appetite, no energy and your eyes and nose start to drip. After some time, the discharge from its eyes and nose starts to get thick, yellow and sticky - a classic sign of distemper. If you did not take your dog to the vet before this symptom appears, you should take it now. Other symptoms of the first stage of distemper are: dry cough, diarrhea and pus blisters on the stomach. The second phase of distemper is even more frightening because the disease can strike and affect the brain to the backbone. A dog may drool at this stage often shake his head or act as if she has a strange taste in mouth. Sometimes it has convulsions, making it him to walk in circles, fall and strike the air. Then looks confused, shrinking front of people. When the disease reaches this stage, there is little hope of life.
Dogs that survive often have permanent neurological sequel. The virus can also migrate to the lungs causing pneumonia, conjunctivitis and inflamed nasal passages (rhinitis) and it also spread to the skin becoming it thicker especially in the soles of the paw. Distemper is more likely to infect puppies from nine to twelve weeks especially if they are in a place with many other dogs. If your dog was diagnosed your veterinarian will give intravenous fluids to replace what it lost with medications to control the diarrhea, vomiting and antibiotics to combat secondary infections.

Distemper Virus
Infectious Canine Hepatitis - This is a viral disease spread by contact. Mild cases last from one to two days with mild fever symptoms and low amount of white blood cells. Puppies from two to six weeks of age can suffer from a form of the disease that comes on quickly. It causes fever, tonsils are swollen and their stomachs hurt. They can quickly go into shock and even die. The attack is fast and unexpected: the dog can be fine one day and suddenly go into shock. The most common form of hepatitis infectious occurs in puppies when they are six to ten weeks. They show the usual signs of fever, lack of energy and swollen tonsils. A puppy whose immune system responds well begins to recover from four to seven days. In severe cases the virus attacks the blood vessel walls and the dog begins to have bleeding from the mouth, nose, rectum and urinary tract. If the dog has infectious hepatitis will need intravenous fluids, antibiotics and even need a blood transfusion.
Hepatitis
Leptospirosis - This bacterium causes a disease that is caused by a spirochete which is a type of bacterium with a spiral narrow shape. The spirochete of leptospirosis pass through the urine of infected animals and enter in the dog's body through an open sore on its skin or even when it eats or drinks something contaminated by infectious urine (rat). The leptospirosis signs are not pleasant. Initially, symptoms include fever, depression, lethargy and loss of appetite. The disease attacks the kidneys, so an infected dog may walk all twisted because its kidneys hurt. As the infection progresses, there are ulcers in its mouth and tongue beyond its tongue gets a thick brown coating. The dog feels pain to eat because its mouth is full of injuries and may even be bleeding. Its stools has blood, it feels very thirsty so it drinks lots of water. Besides all this, he would probably be vomiting and with lot of diarrhea, too.
The treatment of leptospirosis requires hospitalization because it needs antibiotics and other drugs to control vomiting and diarrhea and a dog with advanced symptoms lose too much fluid and need to be hydrated. Second, leptospirosis is a zoonoses and it can infect people. Dogs with leptospirosis should be handled carefully for up to one year.

Leptospirosis
Parvovirus - A highly contagious disease that can be spread through the paws, fur, saliva and feces of an infected dog. Puppies under five months are particularly harshly affected by parvovirus, with more chances to die. The signs begin to emerge from three to fourteen days after a dog has had contact with it. Parvovirus can take two forms: the most common is characterized by severe diarrhea, and other rare form, for injury to the heart muscle.

Parvovirus
A dog with parvovirus is literally sick. If the disease reaches its intestines, it will be severely depressed, with vomiting, abdominal pain, high fever, bloody diarrhea and poor appetite. Few diseases cause this wide variety of serious symptoms. When the parvo goes to the heart, the puppies stop eating and have trouble in breathing. Usually they die quickly, but even when they recover they are likely to have congestive heart failure, which usually kills them.
There are vaccines available against parvo, but between six weeks and five months, the cubs are especially vulnerable to illness, even if they were vaccinated. The reason is complex. At birth, puppies get their immunity passively through the mother's milk. Whatever the diseases that the mother has had or against it has been vaccinated the puppies get protection as well. The effect of these maternal antibodies fades after weaning but may still be strong enough to interfere with the action of the parvovirus vaccine. With any protection at full strength, the virus can pass. Nevertheless, it does not mean you should stop vaccinating a puppy against parvo. The virus is difficult to kill. The virus can last from weeks to months in the environment. If your dog had parvo, thoroughly disinfect all, using one part chlorine bleach mixed with 30 parts water.
Rabies - it is known for thousands of years the rabies is mentioned in Mesopotamia and the writings of Aristotle and Xenophon. Some areas of the world - especially Australia, Britain, Iceland, Japan and the Scandinavian nations - ruled for the extermination of rabies through quarantines on incoming animals, but it is found anywhere in the world.
Rabies
The virus enters the body through a wound, usually in the saliva left for a bite. It can infect and kill any warm-blooded animal, including humans. Depending on the country, the animals most likely to transmit rabies are raccoons, skunks, bats and foxes. In 2004, a total of 6,844 reported cases of rabies, 94 cases were reported in dogs.
Rabies has two forms. One is described as furious and another one is called paralytic. Paralytic rabies is usually the final stage, with death at the end. A dog on furious stage of rabies can last from one to seven days, passing through various behaviors, and may be agitated or nervous, and sensitive to light and touch. Its breathing becomes rapid and breathless, making it to dribble at the mouth. Another sign of rabies is a "change of personality. As the rabies virus does its damage in the central nervous system, the dog has difficulty walking and moving. Never try to approach one who is behaving unusually. Be extremely cautious around a dog you know to be acting strangely.
Because rabies is fatal, veterinarians of the public health recommend euthanasia. A dog that appears healthy but has bitten someone must be kept isolated for ten days to see if the signs of rabies develop. A non-vaccinated dog that has been exposed to rabies must be euthanized or strictly confined for six months, receiving a rabies vaccine a month before being released from quarantine. If a vaccinated dog is exposed to rabies, it should receive a booster dose at once, be confined and closely observed for 90 days. Unfortunately, the only way to confirm if a dog has rabies is to examine its brain (specifically, the fabric of its central nervous system) - which means the dog can not be alive.
Rabies is a serious disease. To protect your dog against rabies, you should vaccinate it to three months, again a year later and then every three years. If you are bitten by a rabid animal - or an animal you can not confirm for sure that did not rabies - immediately clean the bite wound with soap and water. Then call your doctor for help.

DOG WITH RABIES (RABIES SIGNALS EXPOSED)
Distemper usually happens in two phases. Three to fifteen days after exposure to virus, the dog develops a fever, poor appetite, no energy and your eyes and nose start to drip. After some time, the discharge from its eyes and nose starts to get thick, yellow and sticky - a classic sign of distemper. If you did not take your dog to the vet before this symptom appears, you should take it now. Other symptoms of the first stage of distemper are: dry cough, diarrhea and pus blisters on the stomach. The second phase of distemper is even more frightening because the disease can strike and affect the brain to the backbone. A dog may drool at this stage often shake his head or act as if she has a strange taste in mouth. Sometimes it has convulsions, making it him to walk in circles, fall and strike the air. Then looks confused, shrinking front of people. When the disease reaches this stage, there is little hope of life.
Dogs that survive often have permanent neurological sequel. The virus can also migrate to the lungs causing pneumonia, conjunctivitis and inflamed nasal passages (rhinitis) and it also spread to the skin becoming it thicker especially in the soles of the paw. Distemper is more likely to infect puppies from nine to twelve weeks especially if they are in a place with many other dogs. If your dog was diagnosed your veterinarian will give intravenous fluids to replace what it lost with medications to control the diarrhea, vomiting and antibiotics to combat secondary infections.

Infectious Canine Hepatitis - This is a viral disease spread by contact. Mild cases last from one to two days with mild fever symptoms and low amount of white blood cells. Puppies from two to six weeks of age can suffer from a form of the disease that comes on quickly. It causes fever, tonsils are swollen and their stomachs hurt. They can quickly go into shock and even die. The attack is fast and unexpected: the dog can be fine one day and suddenly go into shock. The most common form of hepatitis infectious occurs in puppies when they are six to ten weeks. They show the usual signs of fever, lack of energy and swollen tonsils. A puppy whose immune system responds well begins to recover from four to seven days. In severe cases the virus attacks the blood vessel walls and the dog begins to have bleeding from the mouth, nose, rectum and urinary tract. If the dog has infectious hepatitis will need intravenous fluids, antibiotics and even need a blood transfusion.

Leptospirosis - This bacterium causes a disease that is caused by a spirochete which is a type of bacterium with a spiral narrow shape. The spirochete of leptospirosis pass through the urine of infected animals and enter in the dog's body through an open sore on its skin or even when it eats or drinks something contaminated by infectious urine (rat). The leptospirosis signs are not pleasant. Initially, symptoms include fever, depression, lethargy and loss of appetite. The disease attacks the kidneys, so an infected dog may walk all twisted because its kidneys hurt. As the infection progresses, there are ulcers in its mouth and tongue beyond its tongue gets a thick brown coating. The dog feels pain to eat because its mouth is full of injuries and may even be bleeding. Its stools has blood, it feels very thirsty so it drinks lots of water. Besides all this, he would probably be vomiting and with lot of diarrhea, too.
The treatment of leptospirosis requires hospitalization because it needs antibiotics and other drugs to control vomiting and diarrhea and a dog with advanced symptoms lose too much fluid and need to be hydrated. Second, leptospirosis is a zoonoses and it can infect people. Dogs with leptospirosis should be handled carefully for up to one year.

Parvovirus - A highly contagious disease that can be spread through the paws, fur, saliva and feces of an infected dog. Puppies under five months are particularly harshly affected by parvovirus, with more chances to die. The signs begin to emerge from three to fourteen days after a dog has had contact with it. Parvovirus can take two forms: the most common is characterized by severe diarrhea, and other rare form, for injury to the heart muscle.

A dog with parvovirus is literally sick. If the disease reaches its intestines, it will be severely depressed, with vomiting, abdominal pain, high fever, bloody diarrhea and poor appetite. Few diseases cause this wide variety of serious symptoms. When the parvo goes to the heart, the puppies stop eating and have trouble in breathing. Usually they die quickly, but even when they recover they are likely to have congestive heart failure, which usually kills them.
There are vaccines available against parvo, but between six weeks and five months, the cubs are especially vulnerable to illness, even if they were vaccinated. The reason is complex. At birth, puppies get their immunity passively through the mother's milk. Whatever the diseases that the mother has had or against it has been vaccinated the puppies get protection as well. The effect of these maternal antibodies fades after weaning but may still be strong enough to interfere with the action of the parvovirus vaccine. With any protection at full strength, the virus can pass. Nevertheless, it does not mean you should stop vaccinating a puppy against parvo. The virus is difficult to kill. The virus can last from weeks to months in the environment. If your dog had parvo, thoroughly disinfect all, using one part chlorine bleach mixed with 30 parts water.
Rabies - it is known for thousands of years the rabies is mentioned in Mesopotamia and the writings of Aristotle and Xenophon. Some areas of the world - especially Australia, Britain, Iceland, Japan and the Scandinavian nations - ruled for the extermination of rabies through quarantines on incoming animals, but it is found anywhere in the world.

The virus enters the body through a wound, usually in the saliva left for a bite. It can infect and kill any warm-blooded animal, including humans. Depending on the country, the animals most likely to transmit rabies are raccoons, skunks, bats and foxes. In 2004, a total of 6,844 reported cases of rabies, 94 cases were reported in dogs.
Rabies has two forms. One is described as furious and another one is called paralytic. Paralytic rabies is usually the final stage, with death at the end. A dog on furious stage of rabies can last from one to seven days, passing through various behaviors, and may be agitated or nervous, and sensitive to light and touch. Its breathing becomes rapid and breathless, making it to dribble at the mouth. Another sign of rabies is a "change of personality. As the rabies virus does its damage in the central nervous system, the dog has difficulty walking and moving. Never try to approach one who is behaving unusually. Be extremely cautious around a dog you know to be acting strangely.
Because rabies is fatal, veterinarians of the public health recommend euthanasia. A dog that appears healthy but has bitten someone must be kept isolated for ten days to see if the signs of rabies develop. A non-vaccinated dog that has been exposed to rabies must be euthanized or strictly confined for six months, receiving a rabies vaccine a month before being released from quarantine. If a vaccinated dog is exposed to rabies, it should receive a booster dose at once, be confined and closely observed for 90 days. Unfortunately, the only way to confirm if a dog has rabies is to examine its brain (specifically, the fabric of its central nervous system) - which means the dog can not be alive.
Rabies is a serious disease. To protect your dog against rabies, you should vaccinate it to three months, again a year later and then every three years. If you are bitten by a rabid animal - or an animal you can not confirm for sure that did not rabies - immediately clean the bite wound with soap and water. Then call your doctor for help.

DOG WITH RABIES (RABIES SIGNALS EXPOSED)
Heat stroke - The summer can be dangerous. Playing or exercising a dog in high temperatures can be fatal for these animals. Prevention is the best way to protect your pet. Do your best to reduce them or eliminate them. Keep pets cool, calm in the hottest part of the day. Help your pet to stay healthy by following these simple guidelines.
Any animal can suffer a heat stroke. However, they are particularly susceptible:
• Animals very young or very old.
• Animals with a history of heat strokes.
• Animals with short snout.
• Animals with excess weight.
• Pets with cardiovascular or respiratory problems.
To prevent heat stroke: :
• Keep clean water available and fresh.
• When the animal is kept in a kennel or enclosure you must make sure that there is ventilation and adequate air circulation.
• When you are away from home must ensure that it has shady places where it can escape.
• Do not allow your pet to make excessive exercise in peak hours.
• NEVER leave your pet locked in a parked car.
Some signs of heatstroke are breathless and salivation, popped out eyes or anxious, it does not respond to your orders, dry skin and very hot, high fever, fast heartbeat, fatigue and weakness.
If the dog suffers a heat stroke, try reducing the temperature gradually immersing it in cold water. Then take your pet dog to the vet immediately.
Leishmaniasis - This disease is transmitted by a mosquito and can be fatal. In some areas it is recommended for prevention throughout the year.

Phlebotomus
Distribution of disease in the world: The leishmaniasis or kala-azar persists today in extremely poor, remote and sometimes politically unstable places which is very hard to take care. Patients have little access to affordable medicines and preventive measures. The disease is endemic in 88 nations, where 350 million people are at risk of infection. Almost all the 500 thousand new cases annually from recurrent epidemics occur in rural areas of the Indian subcontinent (India, Nepal, Bangladesh), Brazil and Sudan.

Map Legend (leishmaniose visceral), 1997.
Leishmaniasis Cycle - The vector insect belongs to the genus Lutzomyia in the Americas and Phlebotomus in the rest of the world. During the blood meal the female sandy fly ingests macrophages infected by Leishmania that in the mosquito gut follow the cycle to its development. Then there occurs contamination of humans and animals through the bite of an infected mosquito.
Leishmania Parasite
Fleas and Ticks - Be alert to signs of parasites that are particularly in warmer weather. Talk to your veterinarian about the various methods of prevention of fleas and ticks and their treatment (sprays, collars, etc.). Make sure that the product used is suitable and safe for your pet. If there is a flea infestation it should be promoted to control the parasite in animals and the places he occupied. If you notice a problem with fleas in your house make sure to change the vacuum bag each time it is used. You may need to purchase special products to get rid of fleas. Some ticks can transmit diseases such as the Ricketesioses. Any tick you find on your pet should be ready and completely removed. Use a clamp to remove carefully the tick making sure to completely remove it from your dog´s head and near its mouth. Ask your veterinarian to show you the correct way to remove the ticks

Ticks

Tick's eggs
Dysplasia - The hip dysplasia is a hereditary disease, a physical change or malformation in the joints, with higher incidence on articulations between the pelvis and hind limbs, called the hip joints. It affects dogs of all breeds, but mostly large breeds. Depending on the extent, it causes discomfort, pain or even serious problems of locomotion. When the female has dysplasia the chances of offspring having it are large and because of that you should take some care and avoid smooth floors to not get the disease worse. Until the age of three months, it is recommended practice moderate exercise in order to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis, one structure of soft tissue that can be strengthened. When it grows, you should avoid obesity and exercise too much, like: exercise your dog riding a bike, forcing it to follow you. One way to prevent the breeding to transmit this disease for the offspring is to diagnose all the specimens by X-rays and avoid the mating of the affected. A dog that has a mild hip dysplasia can live a normal life, but it should not be used for mating and reproduction. Even if the puppy is normal, and its parents are ill, you should not use it for breeding because its puppies can acquire the disease.
Canine Brucellosis - Brucellosis is a disease of the reproductive tract that can also cause abortion in females, infection of sexual organs in males and infertility in both.
It is caused by a bacterium which has several different types and it infects pigs, goats, horses, sheep or dogs.
Although there were isolated incidences records of dogs that are infected by contact with cattle infected with another species of bacteria, the name of the bacterium that infects dogs specifically is called Brucella canis.
The contagion is through the relationship with semen or vaginal discharge of an infected male or female (during mating), by contact with breast secretions and aborted babies, and it can also be through contact with urine or other secretions.
In indoor kennels the disease can be transmitted even by air. It can be contagious to humans and it causes symptoms like the flu.
Symptoms of Canine Brucellosis
Females: Abortion between 45 and 55 days after mating, litters with some dead puppies or dying soon after birth, and in other cases they die at the embryo stage and are reabsorbed in such cases and it may seem that the dog did not become pregnant.
Males: Inflammation of the epididymis, testicles or scrotum (leading to testicular atrophy), infertility due to abnormal sperm and reluctance to mate due to the pain caused by inflammation of the reproductive organs. Males can also cause lesions by licking the painful area
Both sexes: swollen lymph nodes. In some cases may show non-specific signs of poor health. In some rare cases the disease causes damage to the kidneys and the nervous system.
And the most dangerous aspect of the disease is that one when the symptoms are not always seen, that is, in many cases an infected dog may have no outward sign. Infected dogs have normal heat cycles and breed normally, and in many cases a dog infected with brucellosis, after aborting all litter, can conceive and give birth to another litter alive thereafter. The problem is that it can infect any male that it is crossed, and its offspring will be likely carriers of the disease and will infect other dogs so on.
The experts estimate that there is up to 6% of the canine population infected and it happens because of the lost dogs that move in big cities.
There is no vaccine and treatment usually consists of prolonged administration of Tetracycline and Streptomycin can not be effective. The only prevention is to have a full breeding tested before crossing.
A dog that had a positive test for brucellosis should not be mated. Bring an infected animal to a breeding program can destroy years of work to establish a line of blood.
The disease is transmitted to a human being who had improper contact with aborted babies. Therefore, if the person has a dog that abort or have stillborn kittens, puppies dead, membranes, placentas, etc. should be handled with gloves and the area must be disinfected completely. The dog should be tested as soon as possible to brucellosis to see if the disease was the cause of the litter of stillborn.
EYE PROBLEMS
Vision problems of dogs in general are exacerbated with age. Injuries caused by sharp objects, scratches and bites are a constant in veterinary ophthalmology. Corrective surgery of the eyelids in some breeds is performed routinely. The evolution of veterinary science has greatly helped the health of our friends. Most of the problems of the age can be identified through regular monitoring to your veterinarian.
Glaucoma - Glaucoma is characterized by an increase in intraocular pressure due to the formation or obstruction of the drainage angle, pupillary block, luxation or subluxation of the lens. These factors do not cause the elimination of aqueous humor (the substance that fills the camera of the eyes) resulting in increased intraocular pressure. It may also be divided into congenital, primary and secondary.
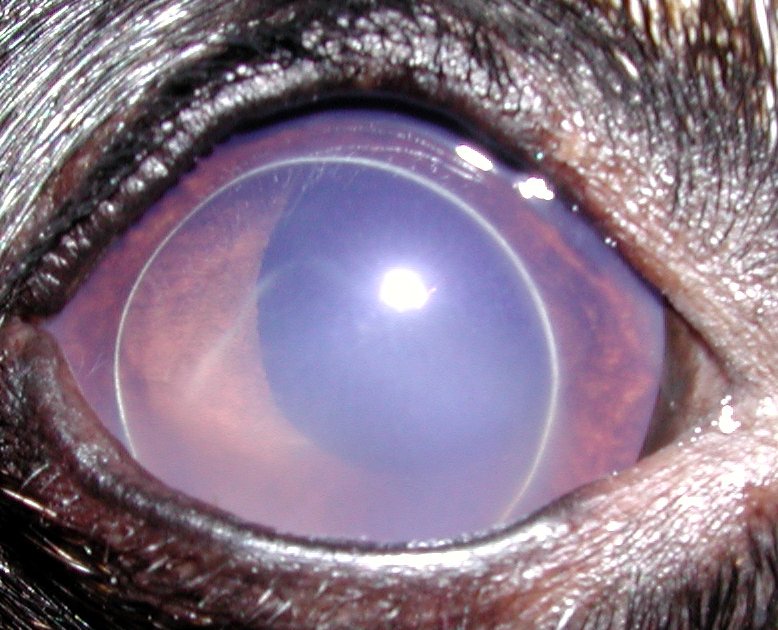
Eye with Glaucoma
The disease is manifested by clinical signs such as corneal edema, congestion of blood vessels eye, mydriasis (pupil dilation), increased IOP and the eyes and pain.
The therapy aims to decrease the production of aqueous humor or even increase its drainage, and can be clinical or surgical, although the latter does not produce good results. The prognosis of glaucoma is very reserved, and the treatment rarely curative.
Cataract - There is opacity in the lens. It can be either small and does not affect vision or may involve the entire lens and cause blindness. Most cataracts, has hereditary and bilateral manifestation. Cataracts can be triggered by diseases such as diabetes and uveitis, through contact with toxic substances and the presence of intraocular tumors. Cataracts can be classified as congenital, juvenile, adult or senile in dogs. The congenital is present at birth. The juvenile occurs in animals less than two years. The cataracts in adults emerge in dogs with two to six years. Senile cataracts develop in dogs with advanced age and are extremely common. The only treatment for cataracts is surgical removal. The removal of cataract surgery is a very delicate and may be some difference in the procedures for clinic to clinic, according to the technique used. A complete ophthalmologic examination is necessary in order to determine whether the dog is a good candidate for surgery. It is also important to conduct an electroretinogram to test the function of the retina. The administration of medication should be started several days before surgery. The surgical technique of choice is that phacoemulsification that uses vibrations by ultrasound to liquefy the cataract which is then aspirated from the eye through a minimal incision. After surgery, the patient is sent home under observation. The success of surgery is dependent on post-surgery treatment. For cataract surgery is successful, the rest of the eye, except the lens, must be healthy. Sometimes, the lens is so opaque, that does not allow direct examination of the retina. The electroretinogram (ERG) is an electronic test that lets you test the function of the retina.
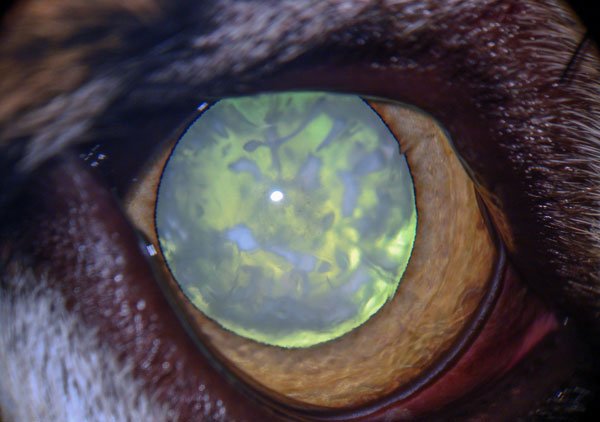
Eye with Cataract
Heartworm - Dogs are infected by parasites that cause serious diseases. These can be installed in various organs but the most common are intestinal worms and heartworm (called Dirofilaria immits). The parasite is named Dirofilaria immitis due to its embryonic form that enters in the body of the dog when it is bitten by mosquitoes that have already bitten an infected host. After about 90 to 100 days of infection, the larva develops and lodges in the area between the right atrium and vena cava of the heart. In adulthood, the parasite reaches about 30 cm long and, after 7 to 8 months of infection, we can find microfilariae circulating in the blood.

Heartworm Stage
Symptoms: The main ones are: cough, short of breath, weight loss, dark tongue, exercise intolerance, and when heart failure is already established, there may be failure of the liver and kidneys, and may even appear abdominal distention and liquid lungs. The cough is usually chronic.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is made based on information obtained from the owner, the clinical examination and laboratory tests that detect the presence of microfilariae in the bloodstream, the chest radiograph, electrocardiogram and an echocardiogram, and tests to study the function of kidney and liver in later stages. It is important to note that the diagnosis can be done and should be done with precision and once the presenting illness the forms of treatment should be exposed. Treatment can be directed to the extinction of adult worms (adulticide treatment) or microfilariae (microfilaricide treatment) associated with the symptomatic treatment of heart failure.
Finally, we can say that the best way to treat canine heartworm disease is through prevention.
Any animal can suffer a heat stroke. However, they are particularly susceptible:
• Animals very young or very old.
• Animals with a history of heat strokes.
• Animals with short snout.
• Animals with excess weight.
• Pets with cardiovascular or respiratory problems.
To prevent heat stroke: :
• Keep clean water available and fresh.
• When the animal is kept in a kennel or enclosure you must make sure that there is ventilation and adequate air circulation.
• When you are away from home must ensure that it has shady places where it can escape.
• Do not allow your pet to make excessive exercise in peak hours.
• NEVER leave your pet locked in a parked car.
Some signs of heatstroke are breathless and salivation, popped out eyes or anxious, it does not respond to your orders, dry skin and very hot, high fever, fast heartbeat, fatigue and weakness.
If the dog suffers a heat stroke, try reducing the temperature gradually immersing it in cold water. Then take your pet dog to the vet immediately.
Leishmaniasis - This disease is transmitted by a mosquito and can be fatal. In some areas it is recommended for prevention throughout the year.

Distribution of disease in the world: The leishmaniasis or kala-azar persists today in extremely poor, remote and sometimes politically unstable places which is very hard to take care. Patients have little access to affordable medicines and preventive measures. The disease is endemic in 88 nations, where 350 million people are at risk of infection. Almost all the 500 thousand new cases annually from recurrent epidemics occur in rural areas of the Indian subcontinent (India, Nepal, Bangladesh), Brazil and Sudan.

Map Legend (leishmaniose visceral), 1997.
Leishmaniasis Cycle - The vector insect belongs to the genus Lutzomyia in the Americas and Phlebotomus in the rest of the world. During the blood meal the female sandy fly ingests macrophages infected by Leishmania that in the mosquito gut follow the cycle to its development. Then there occurs contamination of humans and animals through the bite of an infected mosquito.

Fleas and Ticks - Be alert to signs of parasites that are particularly in warmer weather. Talk to your veterinarian about the various methods of prevention of fleas and ticks and their treatment (sprays, collars, etc.). Make sure that the product used is suitable and safe for your pet. If there is a flea infestation it should be promoted to control the parasite in animals and the places he occupied. If you notice a problem with fleas in your house make sure to change the vacuum bag each time it is used. You may need to purchase special products to get rid of fleas. Some ticks can transmit diseases such as the Ricketesioses. Any tick you find on your pet should be ready and completely removed. Use a clamp to remove carefully the tick making sure to completely remove it from your dog´s head and near its mouth. Ask your veterinarian to show you the correct way to remove the ticks


Dysplasia - The hip dysplasia is a hereditary disease, a physical change or malformation in the joints, with higher incidence on articulations between the pelvis and hind limbs, called the hip joints. It affects dogs of all breeds, but mostly large breeds. Depending on the extent, it causes discomfort, pain or even serious problems of locomotion. When the female has dysplasia the chances of offspring having it are large and because of that you should take some care and avoid smooth floors to not get the disease worse. Until the age of three months, it is recommended practice moderate exercise in order to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis, one structure of soft tissue that can be strengthened. When it grows, you should avoid obesity and exercise too much, like: exercise your dog riding a bike, forcing it to follow you. One way to prevent the breeding to transmit this disease for the offspring is to diagnose all the specimens by X-rays and avoid the mating of the affected. A dog that has a mild hip dysplasia can live a normal life, but it should not be used for mating and reproduction. Even if the puppy is normal, and its parents are ill, you should not use it for breeding because its puppies can acquire the disease.
| Classification of Canine Hip Dysplasia | ||
|---|---|---|
| Degree | Descriptiom | Reproduction |
| HD | No signs of hip dysplasia | Suitable breeding |
| HD+/ | Hip joints close to normal | Suitable breeding |
| HD+ | Mild Dysplasia | Yet Allowed |
| HD++ | Moderate Dysplasia | Not suitable for breeding |
| HD+++ | Severe Dysplasia | Not suitable for breeding |
Canine Brucellosis - Brucellosis is a disease of the reproductive tract that can also cause abortion in females, infection of sexual organs in males and infertility in both.
It is caused by a bacterium which has several different types and it infects pigs, goats, horses, sheep or dogs.
Although there were isolated incidences records of dogs that are infected by contact with cattle infected with another species of bacteria, the name of the bacterium that infects dogs specifically is called Brucella canis.
The contagion is through the relationship with semen or vaginal discharge of an infected male or female (during mating), by contact with breast secretions and aborted babies, and it can also be through contact with urine or other secretions.
In indoor kennels the disease can be transmitted even by air. It can be contagious to humans and it causes symptoms like the flu.
Symptoms of Canine Brucellosis
Females: Abortion between 45 and 55 days after mating, litters with some dead puppies or dying soon after birth, and in other cases they die at the embryo stage and are reabsorbed in such cases and it may seem that the dog did not become pregnant.
Males: Inflammation of the epididymis, testicles or scrotum (leading to testicular atrophy), infertility due to abnormal sperm and reluctance to mate due to the pain caused by inflammation of the reproductive organs. Males can also cause lesions by licking the painful area
Both sexes: swollen lymph nodes. In some cases may show non-specific signs of poor health. In some rare cases the disease causes damage to the kidneys and the nervous system.
And the most dangerous aspect of the disease is that one when the symptoms are not always seen, that is, in many cases an infected dog may have no outward sign. Infected dogs have normal heat cycles and breed normally, and in many cases a dog infected with brucellosis, after aborting all litter, can conceive and give birth to another litter alive thereafter. The problem is that it can infect any male that it is crossed, and its offspring will be likely carriers of the disease and will infect other dogs so on.
The experts estimate that there is up to 6% of the canine population infected and it happens because of the lost dogs that move in big cities.
There is no vaccine and treatment usually consists of prolonged administration of Tetracycline and Streptomycin can not be effective. The only prevention is to have a full breeding tested before crossing.
A dog that had a positive test for brucellosis should not be mated. Bring an infected animal to a breeding program can destroy years of work to establish a line of blood.
The disease is transmitted to a human being who had improper contact with aborted babies. Therefore, if the person has a dog that abort or have stillborn kittens, puppies dead, membranes, placentas, etc. should be handled with gloves and the area must be disinfected completely. The dog should be tested as soon as possible to brucellosis to see if the disease was the cause of the litter of stillborn.
EYE PROBLEMS
Vision problems of dogs in general are exacerbated with age. Injuries caused by sharp objects, scratches and bites are a constant in veterinary ophthalmology. Corrective surgery of the eyelids in some breeds is performed routinely. The evolution of veterinary science has greatly helped the health of our friends. Most of the problems of the age can be identified through regular monitoring to your veterinarian.
Glaucoma - Glaucoma is characterized by an increase in intraocular pressure due to the formation or obstruction of the drainage angle, pupillary block, luxation or subluxation of the lens. These factors do not cause the elimination of aqueous humor (the substance that fills the camera of the eyes) resulting in increased intraocular pressure. It may also be divided into congenital, primary and secondary.

The disease is manifested by clinical signs such as corneal edema, congestion of blood vessels eye, mydriasis (pupil dilation), increased IOP and the eyes and pain.
The therapy aims to decrease the production of aqueous humor or even increase its drainage, and can be clinical or surgical, although the latter does not produce good results. The prognosis of glaucoma is very reserved, and the treatment rarely curative.
Cataract - There is opacity in the lens. It can be either small and does not affect vision or may involve the entire lens and cause blindness. Most cataracts, has hereditary and bilateral manifestation. Cataracts can be triggered by diseases such as diabetes and uveitis, through contact with toxic substances and the presence of intraocular tumors. Cataracts can be classified as congenital, juvenile, adult or senile in dogs. The congenital is present at birth. The juvenile occurs in animals less than two years. The cataracts in adults emerge in dogs with two to six years. Senile cataracts develop in dogs with advanced age and are extremely common. The only treatment for cataracts is surgical removal. The removal of cataract surgery is a very delicate and may be some difference in the procedures for clinic to clinic, according to the technique used. A complete ophthalmologic examination is necessary in order to determine whether the dog is a good candidate for surgery. It is also important to conduct an electroretinogram to test the function of the retina. The administration of medication should be started several days before surgery. The surgical technique of choice is that phacoemulsification that uses vibrations by ultrasound to liquefy the cataract which is then aspirated from the eye through a minimal incision. After surgery, the patient is sent home under observation. The success of surgery is dependent on post-surgery treatment. For cataract surgery is successful, the rest of the eye, except the lens, must be healthy. Sometimes, the lens is so opaque, that does not allow direct examination of the retina. The electroretinogram (ERG) is an electronic test that lets you test the function of the retina.

Heartworm - Dogs are infected by parasites that cause serious diseases. These can be installed in various organs but the most common are intestinal worms and heartworm (called Dirofilaria immits). The parasite is named Dirofilaria immitis due to its embryonic form that enters in the body of the dog when it is bitten by mosquitoes that have already bitten an infected host. After about 90 to 100 days of infection, the larva develops and lodges in the area between the right atrium and vena cava of the heart. In adulthood, the parasite reaches about 30 cm long and, after 7 to 8 months of infection, we can find microfilariae circulating in the blood.

Symptoms: The main ones are: cough, short of breath, weight loss, dark tongue, exercise intolerance, and when heart failure is already established, there may be failure of the liver and kidneys, and may even appear abdominal distention and liquid lungs. The cough is usually chronic.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is made based on information obtained from the owner, the clinical examination and laboratory tests that detect the presence of microfilariae in the bloodstream, the chest radiograph, electrocardiogram and an echocardiogram, and tests to study the function of kidney and liver in later stages. It is important to note that the diagnosis can be done and should be done with precision and once the presenting illness the forms of treatment should be exposed. Treatment can be directed to the extinction of adult worms (adulticide treatment) or microfilariae (microfilaricide treatment) associated with the symptomatic treatment of heart failure.
Finally, we can say that the best way to treat canine heartworm disease is through prevention.